Download Vector Definition Physics SVG, DXF, EPS and PNG Formats.
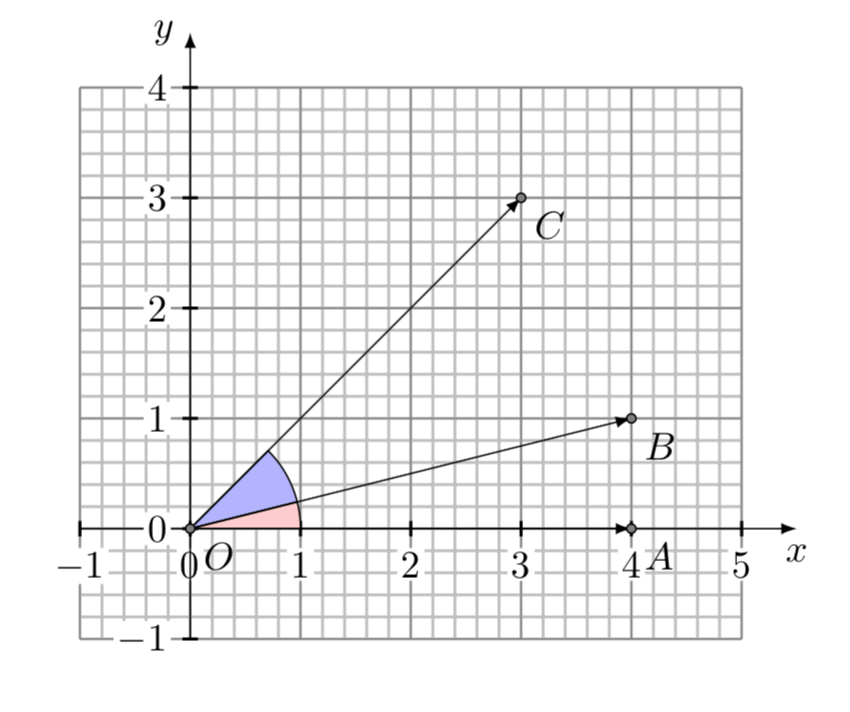
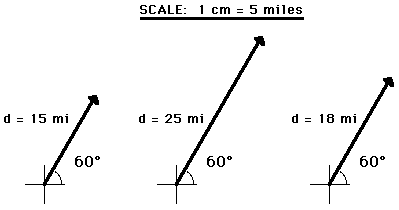
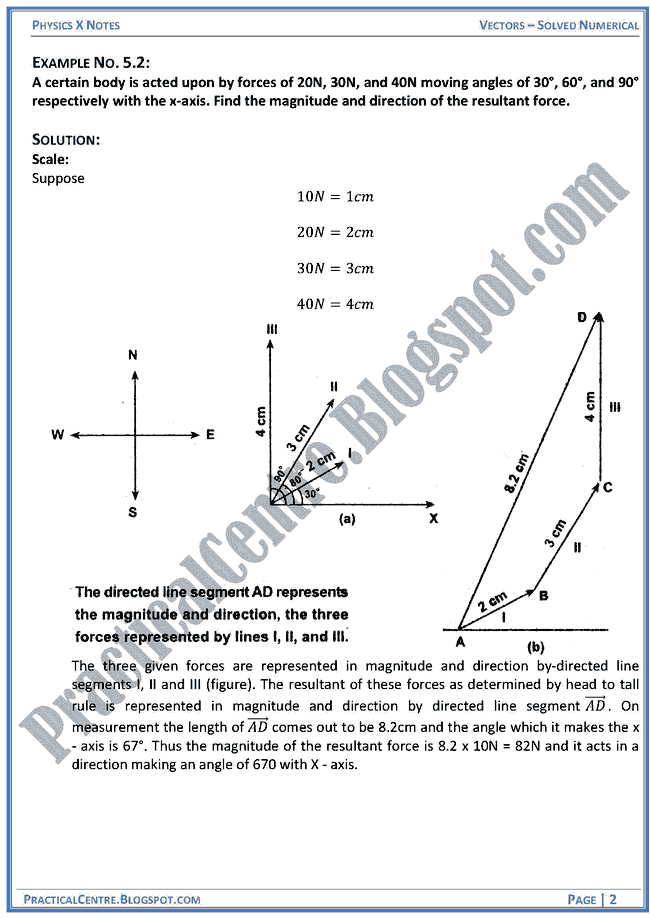
The head of the second vector is placed at the tail of the first vector and the head of the third vector is placed at the tail of the second vector.



Download Link 2
Vector definition physics. A vector quantity has a direction and a magnitude while a scalar has only a magnitude. Visually you see vectors drawn as arrows which is perfect because an arrow has. Its direction and its magnitude. You can not set a vector quantity equal to a scalar quantity.
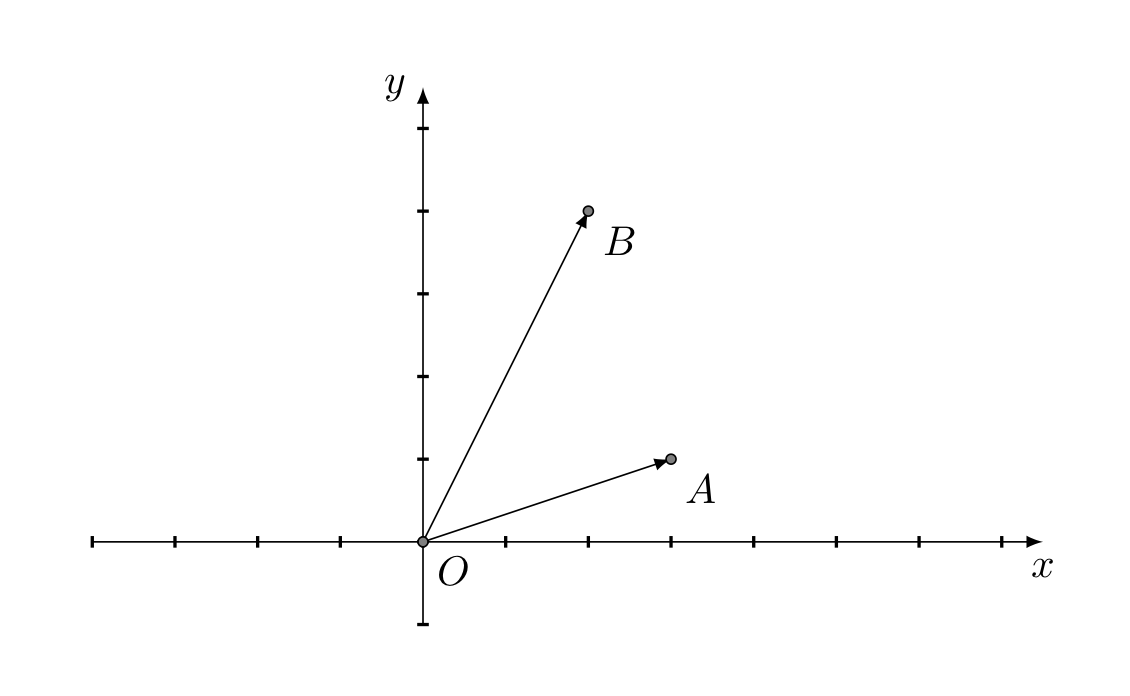
Some examples of vector quantities include force velocity acceleration displacement and momentum. On the other hand a vector quantity is fully described by a magnitude and a direction. A vector is commonly represented by a line segment in a specific direction indicated by an arrow. In mathematics a unit vector in a normed vector space is a vector often a spatial vector of length 1.
Quantities that have only a magnitude are called scalars. The vectors are defined as an object containing both magnitude and direction. You just cant do it. Vector math can be geometrically picturised by the directed line segment.
Vector addition is one of the most common vector operations that a student of physics must master. These are different quantities. Although a vector has magnitude and direction it does not have position. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumflex or hat.
The term direction vector is used to describe a unit vector being used to represent spatial direction and such quantities are commonly denoted as d. When adding vectors a head to tail method is employed. Vector describes the movement of an object from one point to another. Historically vectors were introduced in geometry and physics typically in mechanics before the formalization of the concept of vector spacetherefore one talks often of vectors without specifying the vector space to which.
And so forth until all vectors have been added. If you give a scalar magnitude a direction you create a vector. In physics when you have a vector you have to keep in mind two quantities. All measurable quantities in physics can fall into one of two broad categories scalar quantities and vector quantities.
Vector in physics a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. This equation was in a very recent introductory physics text. It is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantitys magnitude. What is the difference between a scalar and vector.
Vector definition in math and physics in physical science and engineering a vector is a geometric object which has both magnitude or length and direction. A scalar quantity is a measurable quantity that is fully described by a magnitude or amount.