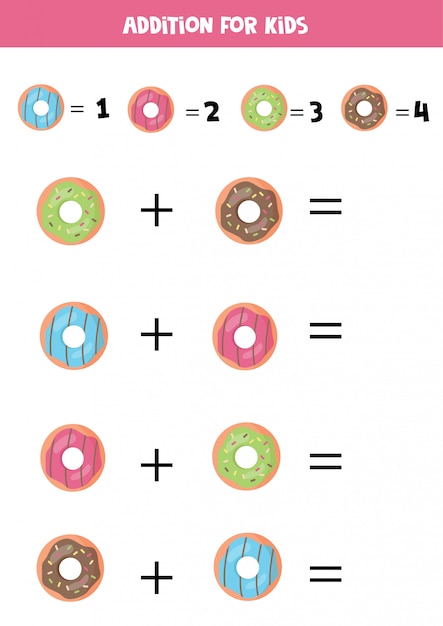Download Vector Addition Example SVG, DXF, EPS and PNG Formats.
Vector addition is the operation of adding two or more vectors together into a vector sum.



Download Link 2
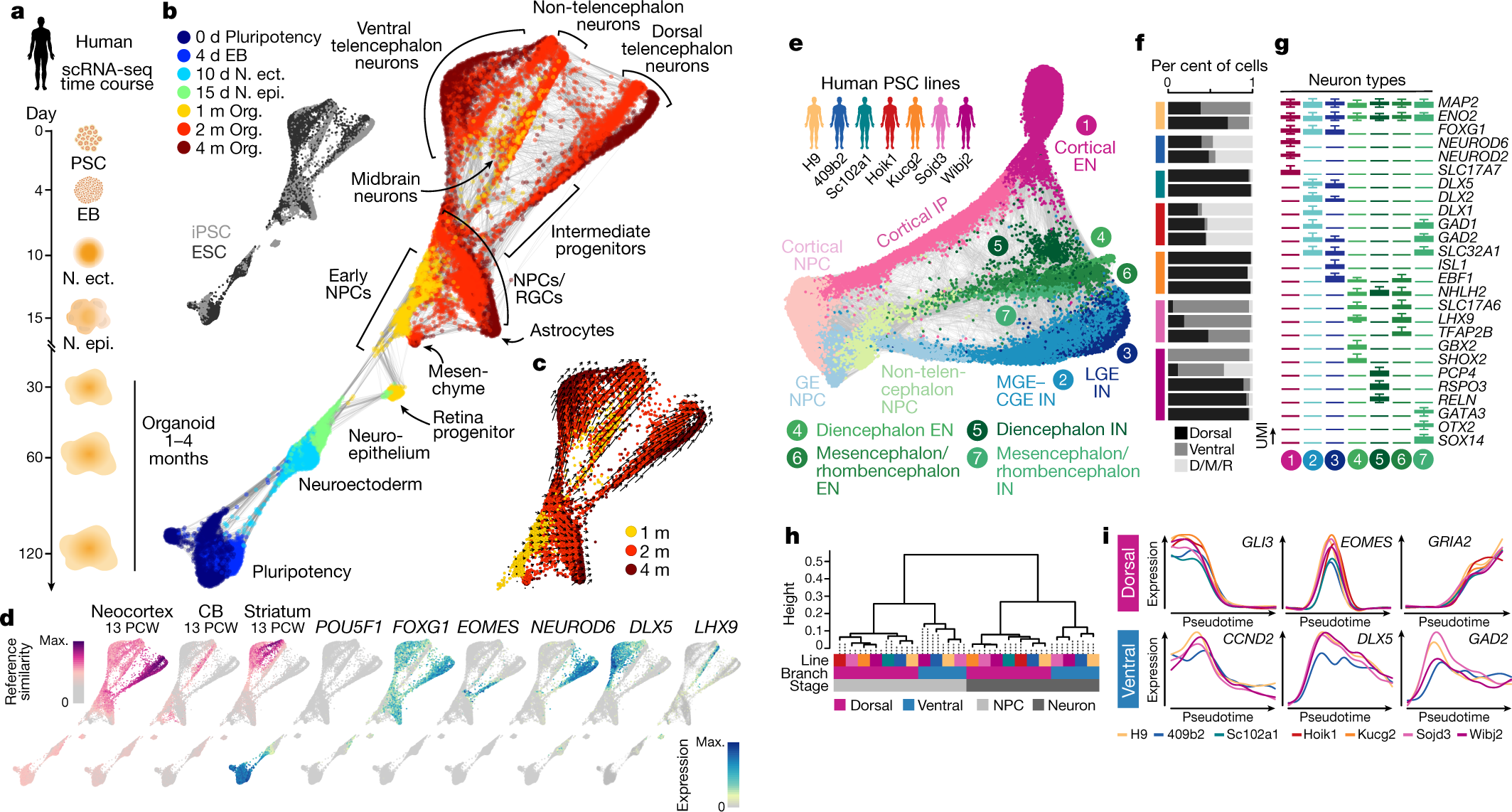
Vector addition example. The statement of parallelogram law of vector addition is that in case the two vectors happen to be the adjacent sides of a parallelogram then the resultant of two vectors is represented by a vector. Furthermore this vector happens to be a diagonal whose passing takes place through the point of contact of two vectors. U v u v change the direction of vector v to get the vector v. Since pqr forms a triangle the rule is also called the triangle law of vector addition.
Statement when two vectors are represented by two sides of a triangle in magnitude and direction were taken in the same order then the third side of that triangle represents in magnitude and direction the resultant of the vectors. P q p q example. So a 50 newton force vector would be an arrow of 5 centimeters in length. The column vector should represent the vector that was drawn.
In cartesian coordinates vector addition can be performed. This angle is the southward angle of rotation that the vector r makes with respect to west. Triangle law of vector addition. Subtract the vector v from the vector u.
Graphically we add vectors with a head to tail approach. Given that find the sum of the vectors. Subtracting a vector is the same as adding its negative. In vector addition the intermediate letters must be the same.
High school physics chapter 5 section 1. For two vectors and the vector sum is obtained by placing them head to tail and drawing the vector from the free tail to the free head. The difference of the vectors p and q is the sum of p and q. A plane is flying along pointing north but there is a wind coming from the north west.
Observe that the angle within the triangle is determined to be 266 degrees using soh cah toa. Triangular law of vector addition. If two vectors are arranged head to tail the triangular law of vector addition is carried out. In mathematics physics and engineering a euclidean vector sometimes called a geometric or spatial vector oras heresimply a vector is a geometric object that has magnitude or length and directionvectors can be added to other vectors according to vector algebraa euclidean vector is frequently represented by a line segment with a definite direction or graphically as an arrow.
So for example with a force vector you could say that every centimeter equals a force of 10 newtons.